- Iterative and incremental.
- Focus on collaboration and customer feedback.
- Pros: Flexibility, faster delivery, better quality.
- Cons: Requires close collaboration, may lack documentation.
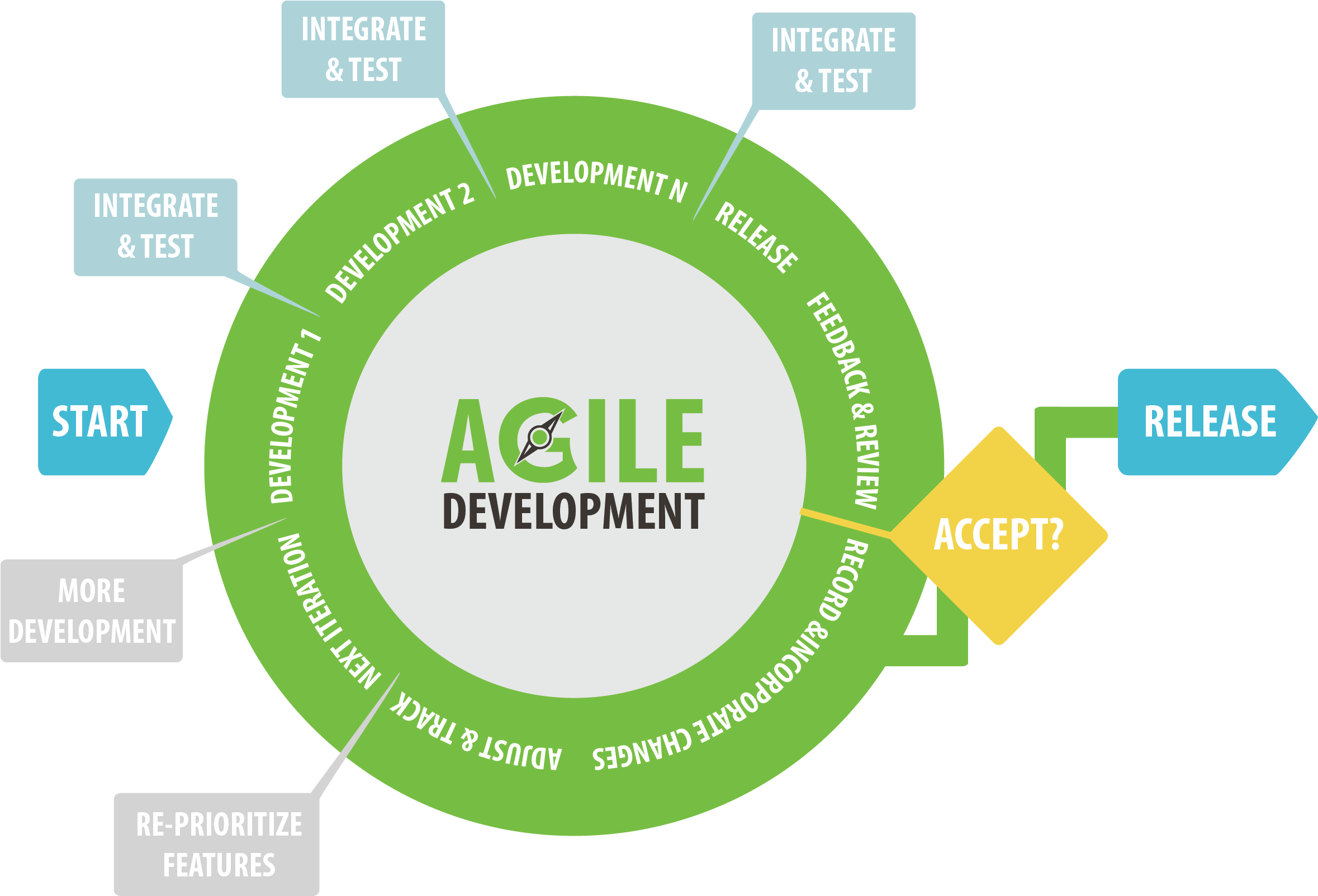
Agile Methodology
📌 Introduction
The Agile methodology is a project management approach that involves breaking the project into phases and emphasizes iterative progress, continuous collaboration, adaptability and improvement . Teams follow a cycle of planning, executing, and evaluating.
Unlike traditional waterfall models, Agile promotes flexibility and continuous feedback.
🛠️ Key Principles of Agile
Agile is based on the Agile Manifesto, which prioritizes:
- Individuals and interactions over processes and tools
- Working software over comprehensive documentation
- Customer collaboration over contract negotiation
- Responding to change over following a plan
🔄 Agile Values
- Customer satisfaction through early and continuous delivery
- Welcoming changing requirements at any stage
- Frequent delivery of working software
- Close collaboration between business stakeholders and developers
- Self-organizing teams
- Continuous attention to technical excellence and good design
- Simplicity and efficiency in development
🏗️ Agile Frameworks
Several frameworks follow Agile principles. Here are the most common ones:
1️⃣ Scrum
Scrum is a lightweight framework with short development cycles known as sprints.
Key Components:
- Scrum Team: Product Owner, Scrum Master, Development Team
- Artifacts: Product Backlog, Sprint Backlog, Increment
- Events: Sprint Planning, Daily Standups, Sprint Review, Sprint Retrospective
2️⃣ Kanban
A visual workflow management system that focuses on continuous delivery.
Key Concepts:
- Work in Progress (WIP) limits to prevent overload
- Pull system where new tasks are started only when capacity allows
- Kanban Board for tracking progress
3️⃣ SAFe (Scaled Agile Framework)
SAFe helps large enterprises implement Agile across multiple teams.
Key Features:
- Aligns business strategy with Agile execution
- Uses Agile Release Trains (ARTs) to synchronize work
- Supports Lean and DevOps principles
4️⃣ Extreme Programming (XP)
XP is focused on engineering practices to improve software quality.
Best Practices:
- Test-Driven Development (TDD)
- Continuous Integration
- Pair Programming
- Refactoring
🔁 Agile vs. Waterfall Methodology
| Feature | Agile | Waterfall |
|---|---|---|
| Flexibility | High, adaptive to changes | Rigid, sequential development |
| Approach | Iterative and incremental | Linear, phase-by-phase |
| Delivery | Continuous, in small releases | Single final delivery |
| Collaboration | High involvement of customers | Limited customer involvement |
| Risk Handling | Low, due to ongoing feedback | High, as testing happens late |
graph TD;
A[Project Initiation] --> B[Backlog Creation]
B --> C[Iteration Planning]
C --> D[Development & Testing]
D --> E[Review & Feedback]
E -->|Approved| F[Release & Deployment]
E -->|Changes Required| B
🎯 Agile Best Practices
- Daily Stand-ups to track progress and resolve issues quickly
- Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) for faster releases
- User Stories & Story Points to prioritize work effectively
- Retrospectives to continuously improve team processes
- Automation to reduce manual efforts and improve efficiency
📝 Practical Hands-On Exercise
Task 1: Create a Kanban Board
- Use Trello/JIRA to create a Kanban board.
- Add columns: To-Do, In Progress, Done.
- Assign team members and track progress.
Task 2: Conduct a Scrum Sprint Simulation
- Choose a small project.
- Define a Product Backlog with at least 5 user stories.
- Run a 2-week sprint and track progress using daily stand-ups.
🎓 Summary
Agile methodology helps teams deliver high-quality software efficiently by promoting collaboration, adaptability, and continuous improvement. Popular frameworks like Scrum, Kanban, and SAFe provide structured ways to implement Agile in various environments.
🚀 Adopting Agile leads to faster development cycles, better stakeholder engagement, and improved project success rates!
🔗 Additional Resources
Real-Life Day-to-Day API Examples
- Booking a cab on Uber or Ola.
- Payment processing via PayPal or Razorpay.
- Fetching weather updates from a weather app.
- Using maps for navigation (Google Maps).
Frontend vs Backend: Understanding the Difference
- Frontend:
- Visible part of an application.
- Technologies: HTML, CSS, JavaScript.
- Frameworks: React, Angular, Vue.js.
- Backend:
- Server-side logic and database management.
- Technologies: Node.js, Python, Java.
- Frameworks: Django, Spring, Express.js.
Stages of Application Development
Roles of Developer
- Write and debug code.
- Implement features as per requirements.
Roles of Tester
- Test the application for bugs and performance issues.
- Ensure the application meets user expectations.
Roles of Database Team
- Design and manage databases.
- Ensure data security and availability.
Roles of DevOps Team
- Automate CI/CD pipelines.
- Manage infrastructure and deployment.
- Monitor and optimize application performance.